What Is The Difference Between Branding and Labelling

Table of Contents
What is Branding?
Understanding Branding
Branding encapsulates the process of assigning meaning to an organization, its products, or services, essentially shaping how consumers perceive and engage with a particular brand. It’s a strategic endeavor employed by businesses to not only facilitate brand recognition but also to influence consumer choices in favor of their offerings over competitors’. At its core, branding serves the purpose of attracting and retaining loyal customers and stakeholders by consistently delivering on the promises made by the brand. It’s achieved through the creation and curation of various elements such as logos, designs, mission statements, and the consistent integration of these components across all marketing communications.
Key Aspects Driving Effective Branding
Consistency stands as a cornerstone in successful branding efforts, ensuring that a unified tone, style, and message resonate across all customer touchpoints, whether online or offline. It’s this coherence that aids in differentiation, allowing brands to carve a distinct identity in a crowded marketplace. Moreover, successful branding endeavors aim to establish an emotional connection with consumers, fostering loyalty by effectively communicating the values, personality, and commitments of the brand.
Elements Comprising Branding Strategies
The foundational components of branding involve the creation of a distinct identity, encapsulated in a name, logo, slogan, and an overarching image that sets the business apart from its competitors. More than just visual elements, these serve as emotional anchors, connecting consumers with the brand on a deeper level.
Packaging’s Role in Branding
Packaging serves as more than just a means to protect and preserve products; it is a critical marketing tool. Beyond functionality, effective packaging design captures attention, communicates brand identity, imparts crucial product information, and significantly influences consumer purchasing decisions. The aesthetics, functionality, and relevance to the target audience are key considerations in designing impactful packaging.
In-Store vs. Online Branding Dynamics
In-store branding focuses on creating experiential encounters for customers, allowing them to physically interact with products and experience the brand environment. It involves strategic positioning of products and props to influence brand perception. On the other hand, online branding revolves around crafting a seamless two-dimensional experience, ensuring consistency in imagery, logos, and brand elements across various digital platforms.
The Emphasis on Consistency in Branding
A consistent brand presence is pivotal in an omnichannel landscape, where customers expect uniformity in branding elements, imagery, and messaging across diverse platforms. Whether online or in-store, maintaining this coherence reinforces brand recall and loyalty among consumers.
What is Labelling?
Understanding Labelling
Labelling involves the display of pertinent information on a product, typically through a label placed on its container, packaging, or the product itself. These labels serve various purposes, including providing essential details about the product and issuing necessary warnings, such as allergen information.
Regulatory laws dictate the type and extent of information that must be conveyed through these labels to ensure safety and compliance. Beyond its regulatory function, labelling significantly contributes to a product’s brand identity and market presence.
In a fiercely competitive market, labelling plays a crucial role in distinguishing products, marking them as part of a specific brand. Labels not only make products stand out but also reinforce brand recognition and association.
Components and Types of Labels
Labels serve as carriers of vital product information, including details like product name, expiry and manufacturing dates, usage instructions, weight, price, etc. They can be categorized into different types based on their complexity and purpose:
Simple Tag: Typically found on local products, these tags offer basic information about product quality or price, such as on items like sugar, wheat, or pulses.
Elaborate or Descriptive Tag: Commonly used by branded products, these labels provide extensive information about product use, performance, features, etc., enhancing consumer understanding and engagement.
Objectives Driving Labelling Strategies
Enhanced Recognition: Making products easily identifiable to consumers.
Differentiation: Setting products or brands apart from competitors in the market.
Consumer Convenience: Providing consumers with necessary information for informed decisions.
Attractiveness: Making products more appealing and desirable to potential buyers.
Compliance: Fulfilling legal requirements and regulatory standards.
Types of Product Labels
Product labels fall into distinct categories, each serving a specific purpose in influencing consumer buying decisions:
Brand Label: Utilizing the brand name or logo as the primary label, directly associating products with the company brand.
Grade Label: Reflecting the quality or grade of the product, indicating standards or classifications.
Informative or Descriptive Label: Furnishing comprehensive details about the product, its usage, benefits, and features, aiding consumers in making informed choices.
Brand Label in Action
Brand labels prominently display the company’s brand name, logo, or trademark without additional information. For instance, automobile manufacturers affix their logos or brand names directly onto vehicles, representing the brand’s identity and reputation.
The relationship between labelling, branding, and packaging is symbiotic, with each element influencing and complementing the others in shaping consumer perceptions and purchase decisions.
The Difference between Branding and Labelling:
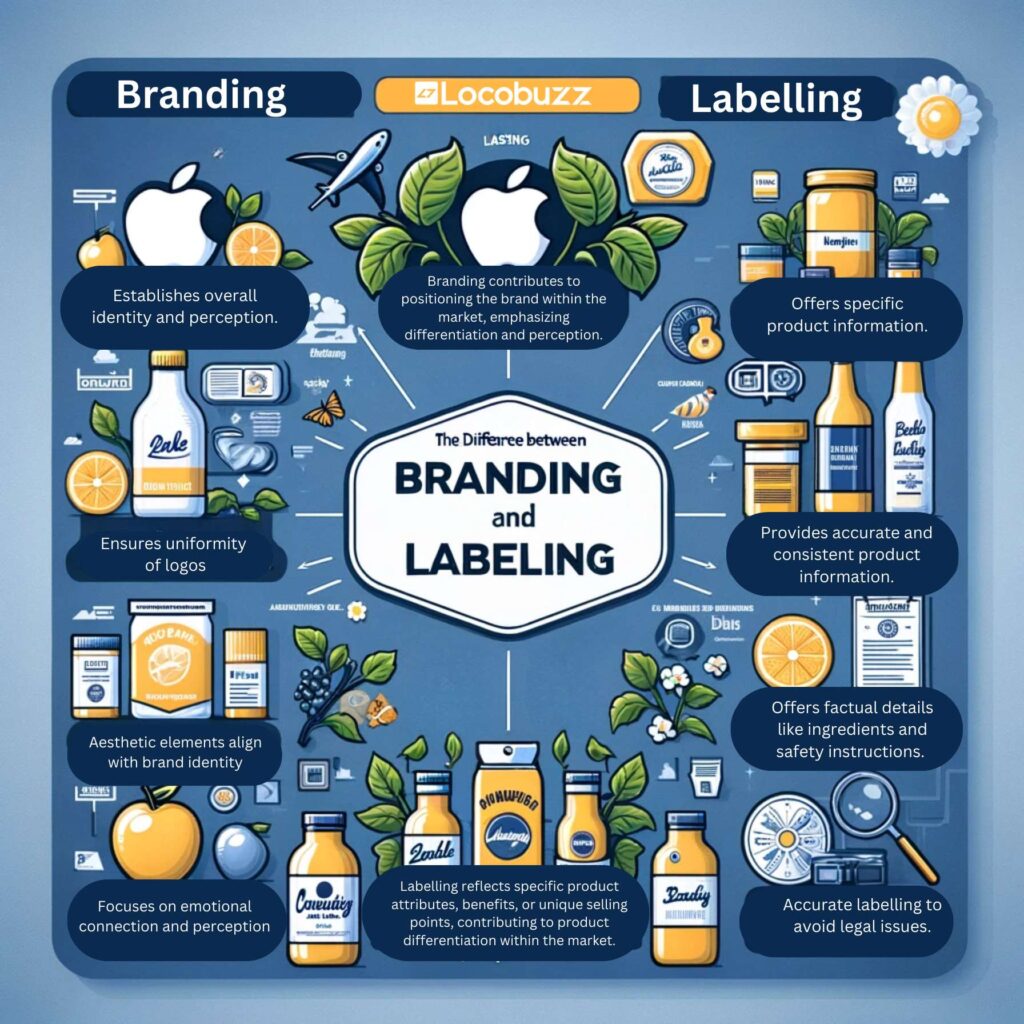
1. Clear Communication:
Branding: Establishes overall identity and perception.
Branding focuses on creating a unique and memorable identity for a product, service, or company. It encompasses a broader narrative and emotional connection, aiming to shape how consumers perceive and relate to the brand. For instance, Apple’s branding emphasizes innovation and user-centric design, creating an aspirational perception among consumers.
Labelling: Offers specific product information.
Labelling, on the other hand, provides specific, detailed information about the product. It includes crucial details such as ingredients, nutritional facts, usage instructions, and safety warnings. This factual information aids consumers in making informed decisions about the product’s suitability and usage.
2. Consistency:
Branding: Ensures uniformity of logos and slogans across various product labels.
Consistency in branding ensures that logos, slogans, and overall brand elements remain uniform across diverse product labels. This consistency reinforces brand recognition and recall, facilitating a strong and recognizable brand identity.
Labelling: Provides accurate and consistent product information.
Consistency in labelling involves offering accurate and consistent information across various product packages. This clarity in information builds consumer trust, ensuring that consumers receive reliable and coherent details regardless of the product variant or packaging.
3. Consumer Trust:
Branding: Focuses on emotional connection and perception, crucial for consumer loyalty.
Branding endeavors to create emotional connections with consumers, fostering loyalty and positive perceptions. It aims to evoke specific feelings or associations linked with the brand, influencing consumer loyalty and purchase decisions.
Labelling: Offers factual details like ingredients and safety instructions.
Labelling, by presenting factual and essential details, contributes to transparency and trust. Accurate information regarding ingredients, safety instructions, and usage guidelines establishes credibility and fosters trust among consumers.
4. Legal Compliance:
Branding: Adherence to regulatory standards contributes to brand credibility.
Adhering to legal and regulatory standards is crucial for brand credibility. Compliance with regulations ensures that the brand maintains a positive image and credibility in the eyes of consumers and stakeholders.
Labelling: Specific guidelines mandate accurate labelling to avoid legal issues.
Various industries, especially those involving food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, have specific guidelines governing labelling practices. Compliance with these guidelines is essential to avoid legal repercussions, including fines or product recalls.
5. Consumer Experience:
Branding: Builds emotional connections; labelling navigates practical aspects of product use.
Branding focuses on creating emotional connections, while labelling addresses the practical aspects of product usage. This comprehensive approach ensures a balanced consumer experience, combining emotional resonance with factual information.
6. Market Positioning:
Branding: Shapes the brand’s position and image in the market.
Branding contributes to positioning the brand within the market, emphasizing differentiation and perception. It helps the brand stand out among competitors by establishing a unique identity and value proposition.
Labelling: Reflects specific product attributes, aiding in product distinction.
Labelling reflects specific product attributes, benefits, or unique selling points, contributing to product differentiation within the market. Clear and accurate labelling highlights the distinct features of the product, aiding in its positioning and appeal.
7. Design and Aesthetics:
Branding: Aesthetic elements align with brand identity, offering visual appeal.
Aesthetic elements in branding, such as design, color schemes, and visual elements, align with the overall brand identity. They contribute to the visual appeal and recognition of the brand across different platforms and products.
Labelling: Balances design with clear presentation of label information.
Labelling’s design strikes a balance between aesthetic appeal and the clear presentation of essential information. The design ensures that the label is visually appealing while effectively communicating product details and instructions.
Benefits of Branding
- Increases Brand Recognition:
Effective branding plays a crucial role in enhancing brand recognition. A well-crafted and consistent brand image helps consumers easily identify and remember your products or services. This increased visibility contributes to brand recall, making it more likely that customers will choose your brand when making purchasing decisions. - Improves Customer Loyalty to Your Brand:
Branding goes beyond just a logo or a tagline; it encompasses the entire customer experience. A strong brand that consistently delivers on its promises fosters trust and reliability. This, in turn, leads to improved customer loyalty. When consumers have positive and consistent interactions with a brand, they are more likely to become repeat customers and advocates for the brand. - Positive Word of Mouth Marketing:
A positive and recognizable brand encourages customers to share their experiences with others. Satisfied customers become brand ambassadors, engaging in positive word-of-mouth marketing. This organic promotion is a powerful tool for attracting new customers, as people often trust recommendations from friends, family, or peers. - Higher Advertising Effectiveness on Customers:
Branding provides a framework for advertising efforts. A well-established brand identity allows marketing messages to resonate more effectively with the target audience. When customers already have familiarity and trust in a brand, advertising efforts become more impactful and can lead to increased engagement and conversion rates. - Lower Price Sensitivity:
Strong branding can contribute to reduced price sensitivity among consumers. When customers associate a brand with quality, reliability, and positive experiences, they may be willing to pay a premium for products or services. This brand loyalty and perceived value can insulate a brand from intense price competition in the market. - More Applicants That Want to Work for Your Brand:
A positive and well-defined brand attracts not only customers but also potential employees. Companies with a strong brand image are more likely to attract top talent. Job seekers often look for organizations that align with their values, and a reputable brand can make your company a more desirable place to work. - Engaged Employees Who Are Proud to Work at Your Company:
A brand is not only an external image but also an internal compass that guides the company culture. Employees who identify with and believe in the brand are more likely to be engaged, motivated, and proud of their association with the company. This sense of pride can lead to increased productivity, creativity, and overall job satisfaction. - Competitive Differentiation:
In a crowded marketplace, differentiation is crucial. A strong brand sets your company apart from competitors. It communicates unique values, qualities, and benefits that distinguish your products or services. This differentiation can be a key factor in influencing consumer choice and building a loyal customer base. - Branding Instills Confidence in Your Company:
A well-established brand instills confidence not only in customers but also in stakeholders such as investors, suppliers, and partners. A consistent brand image reflects stability, reliability, and trustworthiness. This confidence can positively impact financial performance, partnerships, and overall business relationships. Investors, in particular, may see a strong brand as an indicator of long-term viability and success.
Benefits of Labeling
- Describing the Product and Specifying Content:
Labels play a vital role in providing clarity about a product’s attributes, features, and specifications. They serve as a medium to communicate essential information to consumers, ensuring they have a comprehensive understanding of the product. Whether detailing usage instructions, ingredients, or safety precautions, labels contribute to transparency and help consumers make informed choices. Moreover, adherence to regulatory requirements often mandates accurate and detailed labeling to ensure compliance with safety and quality standards. - Identification:
Effective labeling is a key element in brand recognition. Consistent and distinctive labels contribute to the establishment of a brand identity, making it easier for consumers to identify and remember a particular brand amidst a myriad of options. Beyond branding, labels facilitate efficient logistics and inventory management by providing clear identification for tracking, storing, and transporting products. - Grading:
Labels serve as indicators of a product’s quality or grade. In industries like food, grading on labels communicates information about freshness, origin, and adherence to specific quality standards. This not only aids consumers in making choices aligned with their preferences but also builds trust by providing a tangible measure of a product’s value and quality. - Promotion:
A well-designed label is a potent marketing tool. It serves as a platform to highlight key selling points, unique features, and the value proposition of a product. The visual appeal of a label can significantly contribute to a product’s attractiveness on the shelf, catching the consumer’s eye and influencing purchasing decisions. Beyond the physical shelf, labels are instrumental in promotional efforts, conveying messages that resonate with the target audience and enhancing the overall market presence of a product.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Branding is like creating a special feeling or connection between a product and the people who might want to buy it. It’s about making the product stand out and feel special, making people like it more. Labelling, on the other hand, is about giving all the important details about a product. It tells you what’s inside, how to use it safely, and if it follows the rules.
Both branding and labelling are super important for making people choose and trust a product. Brands use emotions and stories to make you like their stuff, while labels give you the facts you need to decide if it’s right for you.
So, it’s really important for businesses to understand the difference between branding and labelling. This way, they can make their products look good and also give people the right information to make smart choices about what they buy. Getting this balance right helps brands become trustworthy and successful.